Why Does The Body Retain Fluids?
The body contains a high percentage of water, which is inside and outside the cells. Under normal conditions, these fluids keep in equilibrium; however, when faced with certain health problems, the body retains fluids.
This situation is called edema and is defined as a palpable swelling produced by the accumulation of extracellular fluid (found outside of cells). It is very common in practice, and the possible causes are very varied. We will detail more about it below.
Why does the body retain fluids?
The whole body needs fluid for its proper functioning. Water is present in the blood, muscles, bones, fat and in every organ. As we have commented, these fluids are present both inside and outside cells.
In turn, the one outside can be divided into the one inside the blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries), and the one outside them in a space called the interstitium.
Permanently, in a healthy body , fluid shifts occur between the different compartments (cells, blood vessels and interstitium), as the body needs it. This constant redistribution of liquids is regulated by a complex balance of pressure gradients (pressure differences).
There are situations in which the balance in fluids can be altered, with the consequent increase in the same in the interstitium. This is what we all know as “fluid retention” or “edema.” It can occur in a generalized or localized manner. Let’s see its possible causes.
Causes of fluid retention
If the body retains fluids it is advisable to request a medical consultation. Although it does not always hide a serious problem, sometimes it is the sign of a disease. Therefore, if the symptom is persistent or appears and reappears regularly, it is better to request the relevant tests.
Heart failure
When the heart is not working properly, it has a hard time pumping blood to other organs. Consequently, there is an accumulation of blood in the venous circulation and the function of the kidneys is reduced.
Both situations generate fluid retention in the venous circulation, with edema that is clinically evident in areas of decline, for example, in the lower extremities when standing. Cardiac enlargement and respiratory distress may also occur.
Hepatic cirrhosis
Liver disease causes fluid retention in the abdomen, called ascites, and also edema in declining areas. According to an article published in An International Journal of Medicine , it is the most common complication of cirrhosis, affecting up to 50% of diagnosed patients.
Nephrotic syndrome and other forms of kidney disease
In situations such as nephrotic syndrome or kidney problems, fluid retention and loss of proteins in the blood occur. High blood pressure and edema are also evidenced in declining body regions. In the morning, the edema of the eyelids is more noticeable. The body retains fluids in a generalized way.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, changes occur in the body at the vascular level, since the volume of blood increases, blood pressure decreases, among other situations whose purpose is to promote the growth of the fetus.
This cardiovascular adaptation usually causes the presence of edema, without these signifying an abnormality or a disease. In any case, pay attention to the presence of shortness of breath, hypertension, cough or fever, as they may indicate a complication.
Venous or lymphatic obstruction
The edema that occurs in these cases can be limited to one limb or body area, since the circulatory alteration is localized. Therefore, we say that it is a focal liquid retention. The most common examples are the following:
- Chronic venous insufficiency.
- Deep vein thrombosis (clot obstruction).
- Chronic lymphangitis (inflammation of the lymphatic ducts).
- Regional lymph node resection.
Standing or sitting for a long time
The body also retains fluids as a result of gravity, especially when sitting or standing for a long period of time. In these cases, it is common to notice swollen legs and feet, especially in the afternoon.
It is not a serious cause and can be improved with measures such as stretching exercises, adequate water consumption and a good diet. In general, we should avoid excessive intake of sodium and processed products.
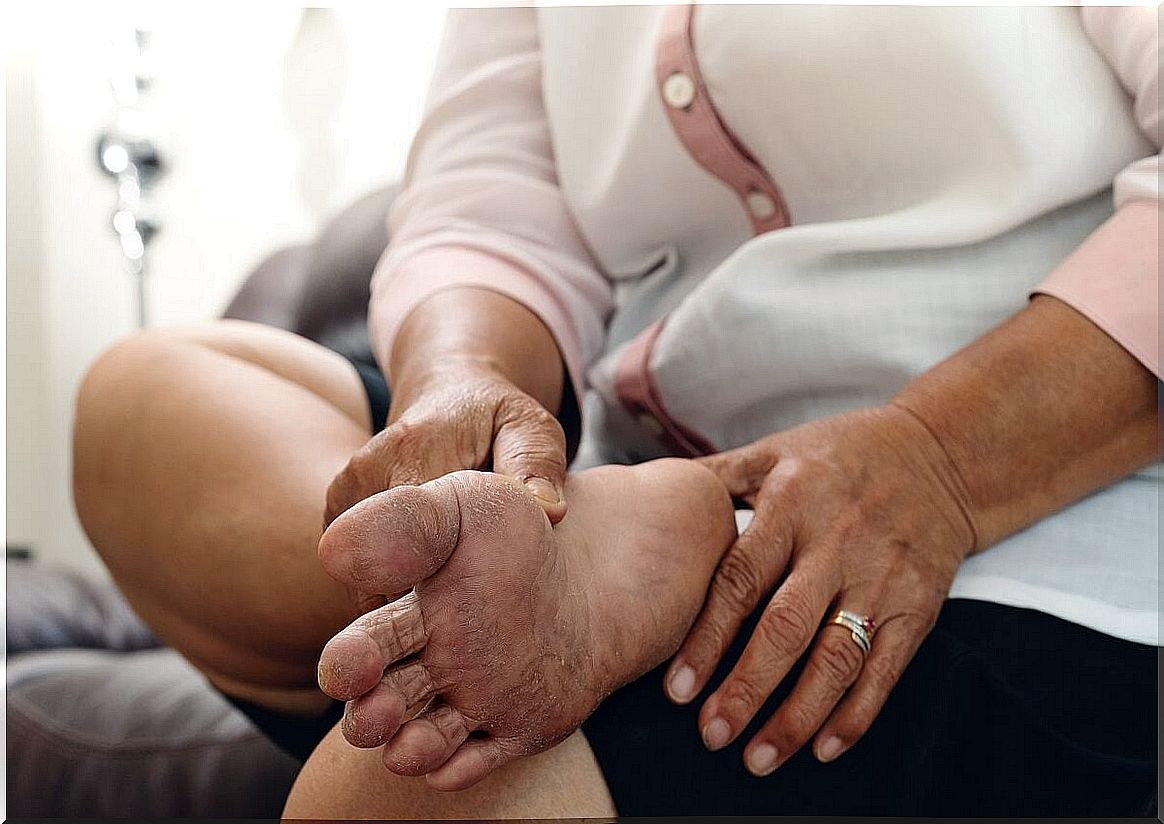
How do you know if the body is retaining fluids?
The alteration of the balance of fluids in the body has several consequences. Whether they are serious or not depends on their cause. However, it is best to seek medical attention to rule out complications or risks. The most common symptoms are the following:
- Weight gain.
- By applying pressure to an area of skin with fluid retention, for at least five seconds, a depression occurs, which persists after it is removed. This is called pitting edema, and it can last a few minutes until it disappears.
- Difficulty removing rings or putting on shoes, especially in the afternoons.
- Swelling in the face, more marked on the eyelids.
- Edema in areas of decline. On legs, when standing; or in the lower back area if you are lying down.
- Stretched or shiny skin.
- Difficulty breathing or walking.
What to do if the body retains fluids?
Symptoms of fluid retention may go away on their own in mild cases. However, if they occur recurrently or severely, it is best to seek medical advice. It should not be ignored that many diseases can have this problem among their symptoms.
In addition, even in mild cases, it is necessary to make lifestyle adjustments to prevent their recurrence. Improving your diet and starting moderate physical exercise will be decisive in dealing with this situation. Also, in some cases the administration of diuretics and other medical treatments is required.