What Is Dysphagia?
Dysphagia is a term that describes a symptom based on swallowing difficulty. According to the Professional Pharmacy magazine, this pathology expresses the inability to progress normally the contents of the mouth to the stomach. This includes both the initiation of swallowing the food and the sensation that the swallowed material is retained in the esophagus.
Due to the multiple causes that can generate this symptom and the discomfort that it produces, knowing the reasons for the appearance of dysphagia and how to combat it is essential. Next, we show you everything you need to know about it.
Types and distribution
According to studies compiled by the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM), the percentage of inhabitants with this symptom in any location is 10%, which is a very common occurrence. This same source compiles that in Spain, the prevalence (percentage of people affected) of dysphagia is 8.3%, regardless of age. However, it was observed that it is much more common in women.
According to sources already cited, this annoying symptom can be divided into two broad categories. We will explain them to you below.
Oropharyngeal dysphagia
In this case, the transfer of the food bolus from the mouth to the esophagus is compromised. According to studies carried out by the World Health Organization (WHO), this variant is much more prevalent in the elderly over 75 years of age, in patients with cerebrovascular accidents and in people who have been intubated as part of medical treatment.
It is a symptom caused by neuromuscular disorders that affect the hypopharynx (the part that is next to and behind the larynx) and the upper esophagus. In the most serious cases, the patient cannot swallow his own saliva, which causes it to accumulate in the oral cavity.
Esophageal dysphagia
Here we refer to a symptom characterized by the difficulty of transporting food through the esophagus until it reaches the stomach. If the patient has impaired swallowing of both solids and liquids, the cause may be a motility disorder.
On the other hand, if you only have problems with solid foods, we are surely facing a mere mechanical obstruction in the esophagus. That is, a growth within the lumen of the organ that stops the descent of food.
Causes of dysphagia
As we have seen, dysphagia is a very general symptom. Scientific studies have tried to calculate its prevalence in the different clinical pictures. Some of the most common are the following.
Neurodegenerative diseases
In neurodegenerative diseases, the presence of oropharyngeal dysphagia is common:
- Bulbar ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) presents this symptom in 100% of cases, because according to the Luzón Foundation, this pathology affects neurons located in the brain stem. This results in difficulties in speaking and swallowing.
- Parkinson’s patients suffer from swallowing difficulties between 35% and 45%. It is not a coincidence, since it is characterized by neuronal death.
- In the case of multiple sclerosis, the prevalence reaches up to 45%.
- Finally, more than 80% of patients with Alzheimer’s present this symptom.
As we have seen, swallowing difficulties are closely related to diseases of neurodegenerative origin. This is not a coincidence, since pharyngeal muscle movements are essential for the transport of food. When neurons fail, they can be disabled.
Other causes
Despite the fact that neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disorders are at the center of suspicion in the face of this annoying symptom, previously cited bibliographic sources emphasize that there are many other pathologies that can cause it. Among them we find the following:
- Achalasia: a rare disorder that consists of the inability of the esophageal sphincter to relax to swallow food.
- Gastroesophageal reflux: rise of food mixed with stomach acids into the esophagus involuntarily.
- Tonsillitis: inflammation of the palatine tonsils, due to viral or bacterial causes.
- Cancers: for example, the appearance of tumors in the esophagus.
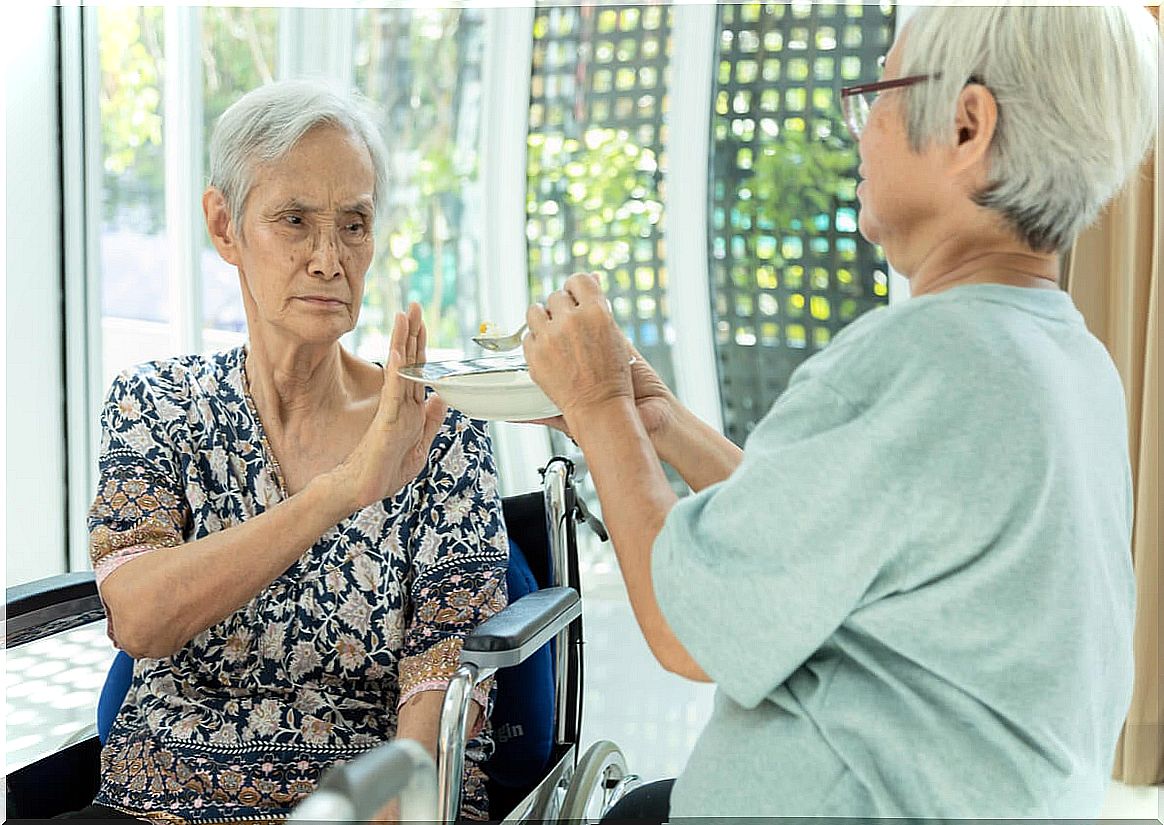

Dysphagia: what to remember?
As we have seen, dysphagia does not respond to a pathology in itself, but is a symptom that warns the patient of an underlying disease. Despite how annoying it may be, official pages, such as Nestle HealthScience, collect various tips to address it.
Some of them are modifying the consistency of foods and drinks to prevent them from being too harsh or dry. Also add milk or sauces to meals so that they acquire a softer consistency or avoid the consumption of fruits and vegetables with seeds.
Unfortunately, this symptom does not have a solution in itself, as the treatment is based on addressing the pathology that causes it. An accurate diagnosis is a fundamental stage that must be conducted by a medical team experienced in this disorder.